Carrier concentration in hall effect formula
Following is the derivation of the Hall-effect. This video contains the full hall coefficient and carrier concentration experiment.

Hall Effect Explained Electric Magnetic Field Drift Velocity Charge Density Calculations Youtube
I -nevA ii Where n is number of electrons per unit volume and A is the area of cross-section of the conductor.

. The DC Hall effect is an important phenomenon in condensed matter physics which allows us to measure properties of a semiconductor. For semiconductor devices in addition to the semiconductors resistivity ρ and carrier mobility μ one of the most important adjustable properties is the carrier concentration np for. Hall Effect is used to find carrier concentration.
Hall mobility µH and carrier concentration n H of charge carriers for each film was calculated using Hall coefficient RH as µH σ x R H cm 2 V. Hot Probe Test to determine Carrier Type p n n i Number of thermally generated Holes equals number thermally generated free electrons Number of free. The area of the cross-section in the sample is A td.
The carrier concentration P obtained from the Hall effect measurements were used to calculate the effective mass m of the carriers by using the. Hall Effect is used to calculate the. If the magnetic field is applied along negative z-axis the Lorentz force moves the charge carriers say electrons toward the y-direction.
µ V x E. Is the total carrier concentration. In our experiment we use the van der Pauw method.
The electron and hole concentration remain constant as long as the temperature remain constant. Sec 3 nH - 1 R H x e cm-3 4. For a given semiconductor the Hall field EH is proportional to the current density Jx and.
Carrier Concentration Calculations p - N AN D -n 0 12 2 12 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 - - -- i A D A D i n N D N A N D N A n p N N N N n 2 np n i 0 2 - N N - n n n A D i - - -2. VH Hall voltage. Hall Effect is used to find whether a semiconductor is N-type or P-type.
Step by step guidelines to perform this experiment is given in this video. T thickness w width. At equilibrium force is downwards due to magnetic field which is equal to upward electric force.
Depending on the type of sample p-type n-type the Hall Voltage will be positive or negative and in case of only one charge carrier electrons or holes determines the transport the charge. N n p n n. The charge carrier mobility is equal to the drift velocity per unit electric field.
For an instrinsic semiconductor such as GaAs we know that n p n e n2 but it is not necessarily the case that p n which would imply zero. Where n is free electron concentration substituting Equation 8117 in 8115 gives. At temperature TK in an intrinsic semiconductor n p ni where ni is called intrinsic.
Since for equation 3 E H V. E E H B e v e V H d B e v V H B v d. Calculation of Hall angle and Mobility of charge carrier.
Applications of Hall Effect. Going back to the Hall effect if the current in the strip is I then from Current and Resistance we know that I nev_dA label1126 where n is the number of charge.
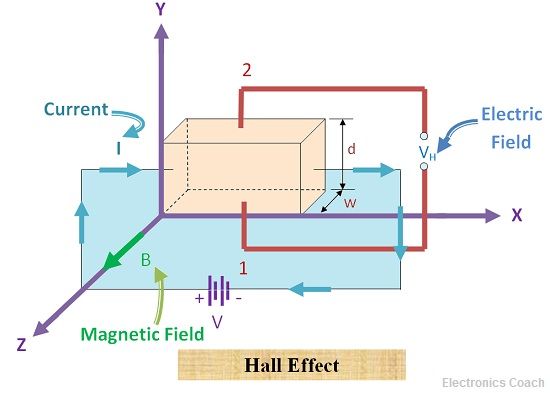
What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach

Physicspaper Shared A Photo On Instagram The Hall Effect Dm Me For Private Tutoring Follow Physicspaper F Physics Notes Physics Memes Hall Effect

The Hall Effect Example Youtube

Hall Effect Sensor And How Magnets Make It Works

Hall Effect Sensor

The Hall Effect And Hall Emf Youtube
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
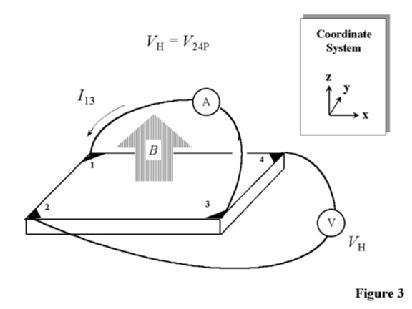
Hall Effect Measurements
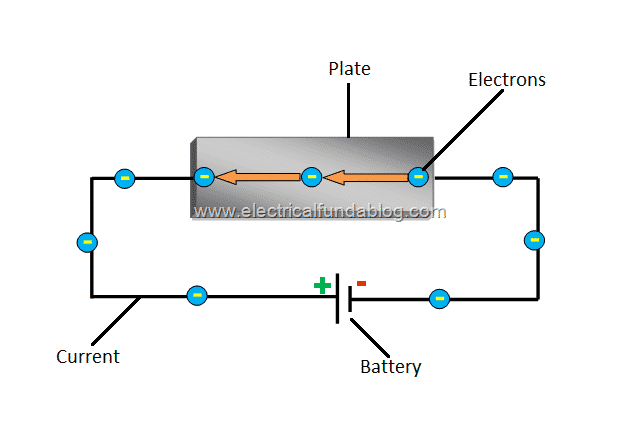
Hall Effect Principle History Theory Explanation Mathematical Expressions And Applications

Hall Effect Principle History Theory Explanation Mathematical Expressions And Applications
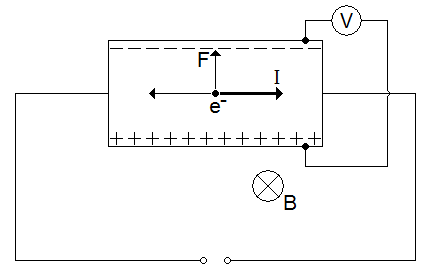
Hall Effect Measurements

What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach

Hall Effect Applications Of Hall Effect Electrical4u
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor
![]()
Schoolphysics Welcome